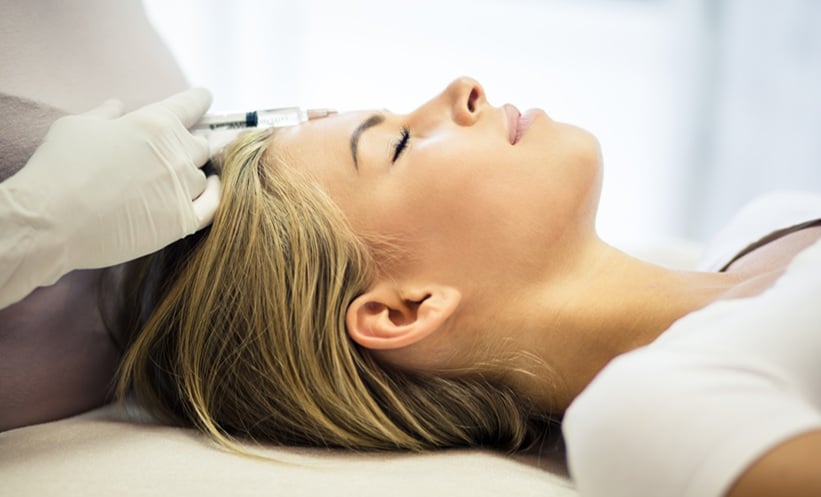
A RECENT clinical trial has revealed notable differences in the effectiveness of various botulinum toxin A formulations when used for cosmetic treatment of glabellar lines. The study, conducted at the University of Pennsylvania, involved 143 women aged between 30 and 65, who were randomly assigned to receive one of four botulinum toxin A treatments: onabotulinum toxin A, abobotulinum toxin A, prabotulinum toxin A, or incobotulinum toxin A. Each participant received a single dose injected into the glabellar region and was followed up at four intervals over 180 days.
The findings highlight that abobotulinum toxin A and prabotulinum toxin A demonstrated the quickest onset of action, with visible effects observed as early as day three. Notably, prabotulinum toxin A and incobotulinum toxin A maintained their effects at the 180-day mark, with prabotulinum toxin A proving significantly more effective at that time point than onabotulinum toxin A. Despite these differences in onset and duration, all four formulations led to significant reductions in glabellar strain and improvements in patient satisfaction up to 90 days following treatment.
The trial also found a direct relationship between the severity of glabellar strain at baseline and the degree of improvement after treatment, suggesting that those with more pronounced lines may experience greater benefits. Interestingly, a reduction in glabellar strain was associated with increased strain in the untreated lateral canthal region, implying a compensatory effect in facial muscle activity.
Overall, this study provides evidence that measurable differences exist between botulinum toxin A products, not only in how quickly they act but also in how long their effects last. These distinctions may help clinicians tailor aesthetic treatments more precisely to align with patients’ goals and expectations.
Reference
Lemdani MS et al. Comparison of botulinum toxin A formulations for glabellar strain treatment in women: a double-blind randomized clinical trial. JAMA Dermatol. 2025;DOI:10.1001/jamadermatol.2025.1335.