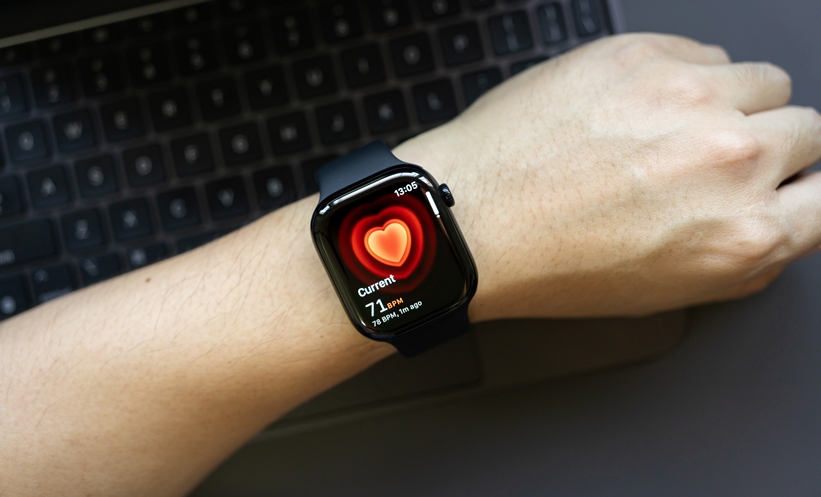
SMARTWATCH screening has been shown to significantly improve atrial fibrillation detection in older, high-risk patients, with researchers reporting substantially higher diagnosis rates compared with standard care.
Wearables Transform Atrial Fibrillation Screening
Atrial fibrillation is the most common sustained cardiac arrhythmia and a major contributor to stroke, heart failure, and premature mortality. However, atrial fibrillation often remains undiagnosed because episodes can be intermittent and asymptomatic. Early identification is essential because timely anticoagulation therapy can reduce stroke risk significantly. Wearable devices equipped with photoplethysmography and electrocardiogram capabilities offer a noninvasive and scalable method to improve detection. Integrating smartwatch monitoring into routine clinical pathways may help clinicians identify atrial fibrillation earlier, particularly among older adults with elevated stroke risk, improving prevention strategies and long-term cardiovascular outcomes across healthcare systems and populations.
Randomised Trial of Atrial Fibrillation Detection
This multicentre randomised controlled trial included 437 patients aged 65 years or older with elevated stroke risk. Participants were assigned to smartwatch monitoring or standard care for 6 months. New onset atrial fibrillation occurred in 21 (9.6%) patients of the intervention group and 5 (2.3%) patients of the control group, representing a risk difference of 7.3 percentage points and hazard ratio of 4.40. The 95% confidence interval was 1.66 to 11.66, and statistical significance was confirmed with P equals 0.001. Several asymptomatic episodes were detected only through smartwatch monitoring. These findings demonstrate substantially improved identification of atrial fibrillation compared with routine clinical care alone in high-risk populations.
The results suggest that wearable screening could reshape atrial fibrillation diagnosis and prevention. Earlier detection enables faster treatment decisions, including anticoagulation, which may reduce stroke risk and improve patient outcomes.
As digital health technologies continue to advance, smartwatch screening may become an important component of cardiovascular prevention, helping to identify hidden disease and improve population health outcomes through proactive and personalised medical care approaches.
Reference
van Steijn NJ et al. Enhanced detection and prompt diagnosis of atrial fibrillation using Apple Watch: a randomized controlled trial. JACC. 2026;DOI:10.1016/j.jacc.2025.11.032.