THE WORLD Health Organization (WHO) has released its World Malaria Report 2025, showcasing significant progress in malaria control while highlighting persistent challenges that threaten global elimination goals. Since 2000, malaria control efforts have averted 2.3 billion cases and 14 million deaths worldwide. However, the disease remains a major global health challenge, with 282 million cases and 610,000 deaths reported in 2024, marking a slight increase from 2023.
Malaria Burden Remains Highest in Africa
The WHO African Region continues to bear the brunt of the malaria burden, accounting for 94% of cases and 95% of deaths globally. Alarmingly, 75% of deaths in the region occur in children under five years old. Five countries (Nigeria, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Ethiopia, Mozambique, and Uganda) contribute more than half of all global cases.
Innovative Tools and Interventions Show Promise
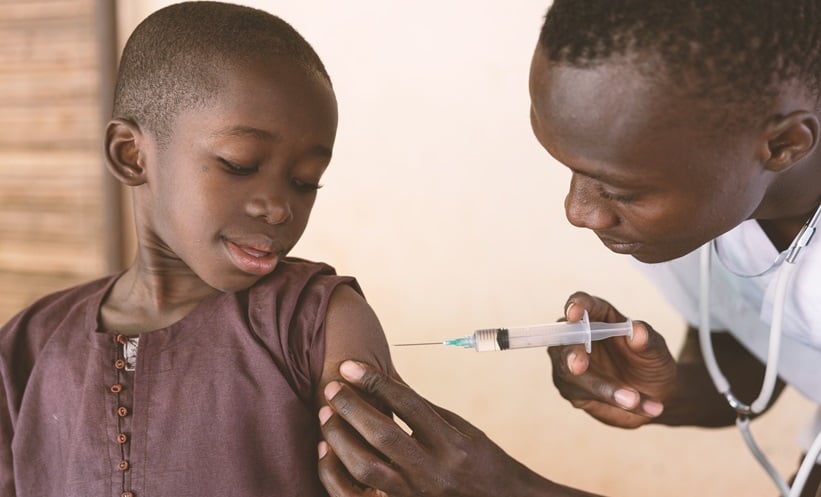
Despite these challenges, innovative tools and interventions are making a difference. The rollout of new-generation insecticide-treated mosquito nets (ITNs), malaria vaccines (RTS,S and R21), and seasonal malaria chemoprevention (SMC) have shown promising results. By the end of 2024, malaria vaccines had been introduced in 17 countries, with over 10.5 million doses delivered, protecting at least 2.1 million children. Additionally, SMC reached 54 million children in 2024, while PMC was implemented in eight countries, benefiting nearly 1 million children under two years old.
However, the fight against malaria faces significant hurdles. Antimalarial drug resistance, insecticide resistance, and the spread of invasive species like Anopheles stephensi threaten progress. Funding shortfalls are also a major concern, with global malaria investments in 2024 reaching only USD 3.9 billion: less than half of the USD 9.3 billion target set by the WHO’s Global Technical Strategy for Malaria 2016–2030.
The report calls for urgent action to reverse the upward trend in malaria cases and deaths. The WHO emphasises the need for strong leadership, community engagement, and sustainable financing to ensure continued progress. The Big Push framework and Yaoundé Declaration aim to strengthen global efforts, expand access to life-saving interventions, and accelerate the path toward malaria elimination. With coordinated action, the WHO asserts that no one should die from malaria.
Reference
World Health Organization (WHO). World malaria report 2025. Available at: https://www.who.int/teams/global-malaria-programme/reports/world-malaria-report-2025. Last accessed 04 December 2025.