BACKGROUND
Long-term survival after lung transplantation remains challenging, with limited research on risk and protective factors. The role of psychosocial wellness and socioeconomic status (SES) are particularly understudied. This study evaluated the impact of pre-transplant surrogate markers of psychosocial health and SES on long-term survival in adult lung transplant recipients.
METHODS
The authors conducted a single-center, retrospective case-control study using the Mayo Clinic lung transplant registry. Cases (survival >6 years) and controls (survival <6 years) were matched by transplant date (±5 years) and indication for transplant, resulting in 190 subjects (63 cases and 127 controls).
Psychosocial health was assessed using the Psychosocial Assessment of Candidates for Transplantation (PACT) score (1–4 scale; ≥2 ultimately required for transplant). Additional variables included proximity to the transplant center, insurance type, marital status, caregiver status, and employment. SES was estimated using two address-based markers: the housing-based SES (HOUSES) index (a novel composite score derived from various housing characteristics where higher scores equal better SES) and the Area Deprivation Index (ADI) at national and state levels (higher scores equal greater deprivation).
Statistical analysis used paired Wilcoxon rank-sum and McNemar’s tests. Results were reported as medians or percentages.
RESULTS
Preliminary data demonstrated that PACT scores and other psychosocial variables had no significant differences between groups. HOUSES index scores were similar (p=0.179), but long-term recipients had significantly higher ADI scores (national: p=0.029; state: p=0.019). Other variables relating to donor and recipient characteristics showed no significant differences (all p>0.05; Table 1).
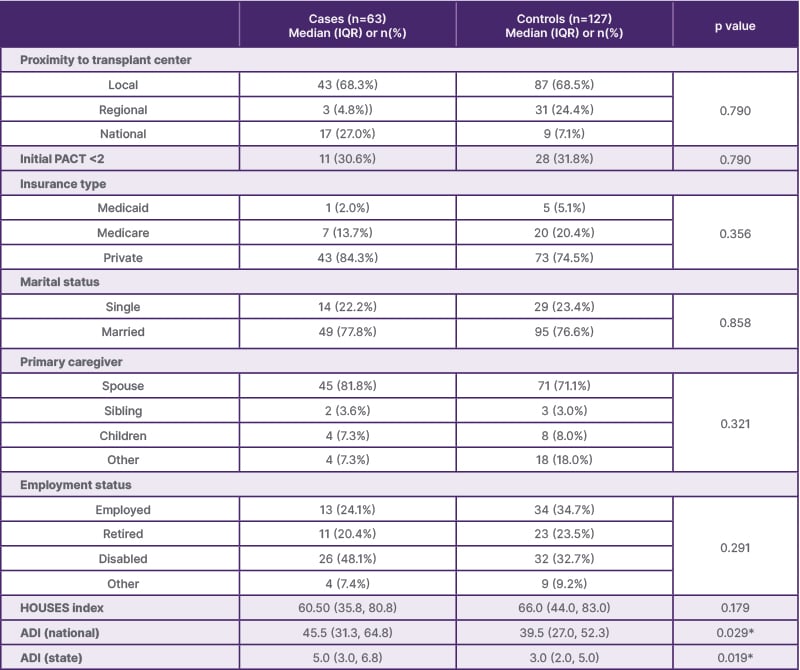
Table 1: Evaluation of risk factors associated with long-term lung transplant survival.
*p<0.05
ADI: Area Deprivation Index; HOUSES: housing-based socioeconomic status; IQR: interquartile range; PACT: Psychosocial Assessment of Candidates for Transplantation.
CONCLUSION
Pre-transplant psychosocial health indicators, including PACT scores, caregiver support, marital status, and proximity to transplant centers, were not linked to long-term survival.
While the HOUSES index was not associated with long-term survival, higher ADI scores correlated with improved survival, suggesting unique protective factors in socioeconomically disadvantaged populations. These findings highlight the complex role of socioeconomic factors in lung transplant outcomes and underscore the need for further research into how specific socioeconomic and environmental factors influence long-term survival.







