NEW research provides critical insights into the phenotypic clusters of pediatric Behçet’s disease, highlighting the complexity and variability of clinical presentations in children with this rare inflammatory condition. The editorial underscores the need for increased awareness and early identification of these clusters to guide more effective diagnosis and treatment.
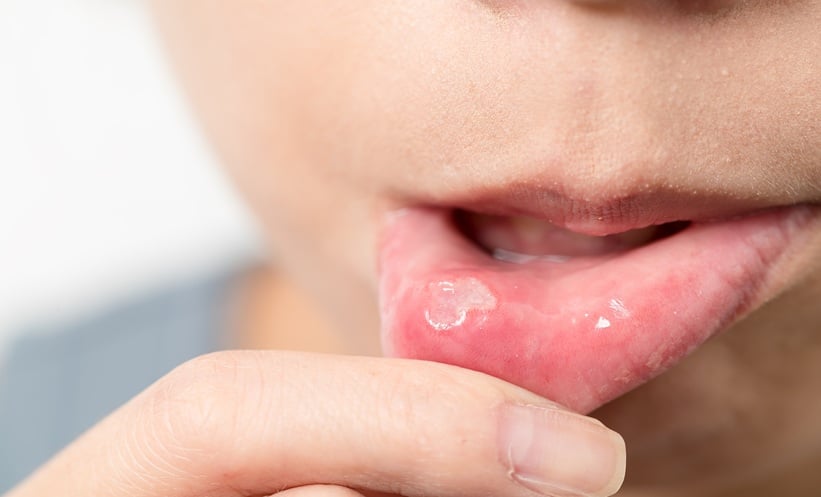
Behçet’s disease (BD), a chronic, multisystem vasculitis, is best known for recurrent oral and genital ulcers, ocular inflammation, and skin lesions. Although more commonly diagnosed in adults, pediatric onset brings unique clinical challenges. The editorial explores how BD manifests in children with increased variability, often presenting with severe or atypical symptoms that can delay diagnosis. Features such as early-onset uveitis and gastrointestinal involvement are more prominent in pediatric cases, distinguishing them from the adult population.
At the pathological level, BD involves widespread inflammation of blood vessels, with immune system dysregulation playing a central role. T-cell activation and cytokine-driven responses contribute to the multisystem involvement seen in patients. Pediatric BD, however, does not follow a single disease course. Instead, it is marked by distinct phenotypic clusters, patterns of clinical features that tend to co-occur in specific subgroups of patients.
Identifying and categorizing these clusters is essential. Doing so may help clinicians anticipate complications, personalize treatment strategies, and improve long-term outcomes. The authors emphasize that current clinical practice would benefit from refined diagnostic criteria and increased research focused on the pediatric population, where the disease may be underrecognized or misdiagnosed due to its diverse presentations.
The editorial calls for clinicians to remain vigilant for signs of pediatric BD in children presenting with unusual inflammatory symptoms and encourages continued research into the biological mechanisms driving these disease patterns.
Reference:
Zou J, Guan JL. Unraveling the complexities of pediatric Behçet’s disease clusters. World J Pediatr. 2025. doi: 10.1007/s12519-025-00933-3. [Online ahead of print]