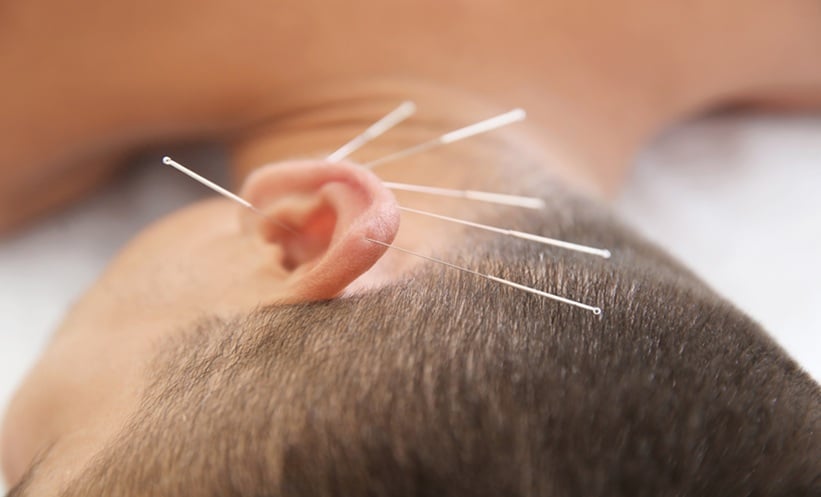
A RECENT study has provided promising evidence that auriculotherapy, a type of acupuncture that stimulates specific points on the ear, may significantly improve urinary incontinence (UI) in men following prostate cancer surgery.
Urinary incontinence affects nearly a third of elderly individuals globally and is particularly common among men after radical prostatectomy, a common treatment for prostate cancer. Postoperative UI can severely impact quality of life and is associated with physical and psychological complications. While pelvic floor muscle training (PFMT) is currently the first-line conservative treatment, its availability is often limited, and many patients find the results inadequate.
In this first-of-its-kind three-arm randomised controlled trial, researchers compared the effectiveness of PFMT alone, PFMT combined with true auriculotherapy, and PFMT with sham (placebo) auriculotherapy. The study aimed to determine whether the addition of auriculotherapy could enhance outcomes for men suffering from postprostatectomy UI.
The findings were encouraging. Patients in the true-auriculotherapy group showed significantly greater improvements in UI severity, pad use, 24-hour leakage episodes, and quality of life compared to those receiving only PFMT. Although the sham-auriculotherapy group showed some improvement, the effects were not statistically significant, suggesting a limited placebo response.
The researchers suggest that the success of true auriculotherapy may be due to its influence on bladder control mechanisms, possibly via the vagus nerve and improved pelvic floor function. Continuous stimulation of ear acupoints appeared to be critical for achieving beneficial effects.
These results indicate that auriculotherapy could be a viable, safe, and non-pharmacological option for managing UI after prostate cancer surgery. However, the researchers caution that larger, longer-term studies are needed to fully understand its mechanisms and confirm its effectiveness across diverse patient populations.
Reference
Zhang Y et al. Effects of auriculotherapy on urinary incontinence in men with prostate cancer: a randomized controlled trial. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2025;25(1):234.