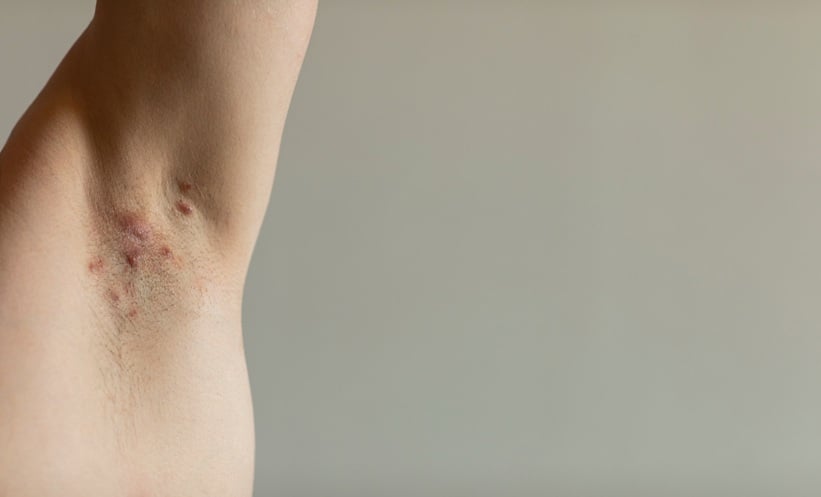
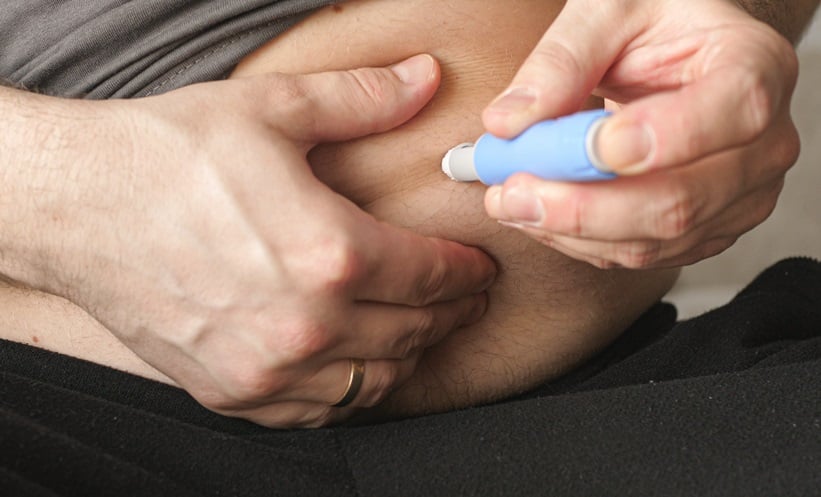
A RECENT network meta-analysis offers important insight into the comparative efficacy, safety, and tolerability of treatments for moderate to severe hidradenitis suppurativa (HS). Drawing on data from 25 randomised clinical trials and involving 5,767 patients across 39 different therapies, the study evaluated a range of targeted treatments, including cytokine inhibitors and other novel immune modulators.
The primary outcome, defined by achieving a 50% reduction in HS symptoms (HiSCR-50), showed that several treatments significantly outperformed placebo. The top-performing therapies included sonelokimab (120 mg and 240 mg), adalimumab (40 mg weekly), lutikizumab (300 mg biweekly), and bimekizumab (320 mg biweekly).
Although no head-to-head active comparator trials were available, most differences between adalimumab and other leading treatments were not statistically significant, suggesting a relatively similar level of efficacy among top contenders. Safety profiles were also comparable: serious adverse events (SAEs) were reported in up to 10% of placebo-treated patients, and between 0% and 8% in those receiving active treatments. The highest treatment discontinuation rate due to adverse events was 15%, observed with ropsacitinib. Most other therapies had discontinuation rates below 5%, including adalimumab, highlighting a generally favourable tolerability profile.
Secondary outcomes, such as achieving HiSCR-75, were also considered, although primary focus remained on HiSCR-50. Importantly, the study supports the use of non-placebo-controlled network meta-analysis to guide treatment strategies in the absence of direct drug comparisons. With many emerging therapies under development for HS, a chronic and often debilitating inflammatory skin disease, this study offers much-needed comparative data to inform clinicians and patients.
As HS remains underdiagnosed and undertreated, findings such as these could help support more informed, patient-specific therapeutic decisions moving forward. The study ultimately highlights the growing potential of biologic therapies in managing moderate to severe HS while emphasising the need for further direct-comparison trials.
Reference
Garg A et al. Efficacy and safety of medical interventions for moderate to severe hidradenitis suppurativa: a living systematic review and network meta-analysis. JAMA Dermatol. 2025;DOI:10.1001/jamadermatol.2025.1976.