NETWORK meta-analysis suggests newer chronic hand eczema monotherapies differ in efficacy based on HECSI score reductions.
Comparative Efficacy of Monotherapies for Chronic Hand Eczema
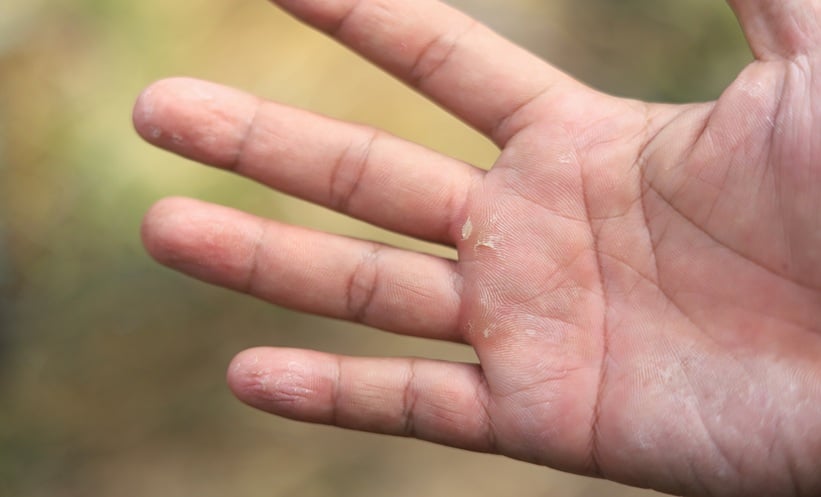
Chronic hand eczema is a common and often disabling occupational condition that is distinct from atopic dermatitis. Symptoms can significantly affect daily function and work, so effective monotherapy options are important in practice. The investigators conducted a network meta-analysis to compare newer chronic hand eczema monotherapies using changes in Hand Eczema Severity Index scores over twelve or sixteen weeks.
After a systematic review, five eligible studies were identified, covering ten active monotherapy comparators. Among these were two treatments approved by the US Food and Drug Administration and the European Medicines Agency for chronic hand eczema, oral alitretinoin 30 mg once daily and topical delgocitinib 20 mg per gram applied twice daily. All analyses were adjusted for baseline disease severity, and additional network meta-regressions explored potential effects of age and sex on treatment response.
Network Meta-Analysis Design and Outcomes
The investigators estimated pairwise relative effects between chronic hand eczema treatments based on mean reductions in Hand Eczema Severity Index scores. They also ranked monotherapies using Surface Under the Cumulative Ranking Curve values to provide an overall probability that each option would be among the most effective. This approach allowed indirect comparison of monotherapies that had not been tested head-to-head within the same trial.
Across the included studies, newer chronic hand eczema monotherapies showed varying degrees of improvement in Hand Eczema Severity Index scores at twelve and sixteen weeks. The authors report that the findings supply comparative information on the relative efficacy of both approved and emerging therapies. In the absence of prior network meta-analyses for chronic hand eczema, these results may help clinicians interpret trial data and position treatments within an evolving therapeutic landscape.
The study highlights the need for further high-quality comparative evidence in chronic hand eczema and supports more informed clinical decision making when selecting monotherapy for individual patients.
Reference: Gupta AK et al. Comparative Efficacy of Monotherapies for Chronic Hand Eczema: A Network Meta-Analysis Study. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2025;24(12):e70552.