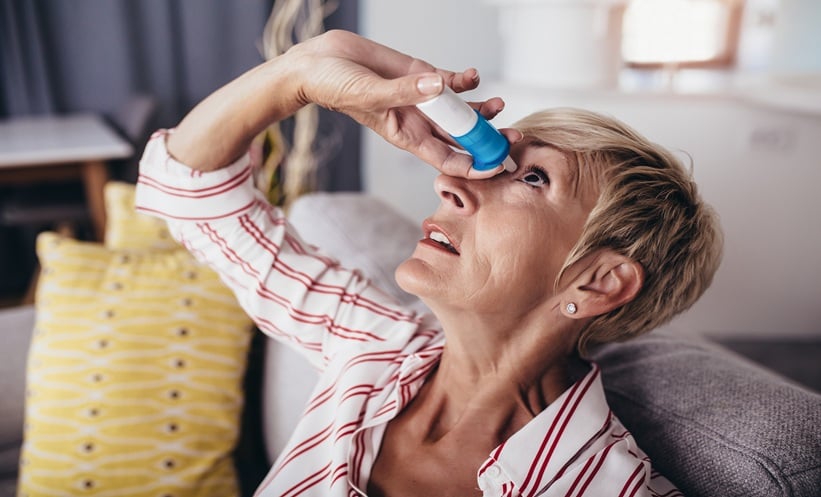
EYE drop pain during routine exams may offer more than momentary discomfort, it could serve as an early marker of dry eye syndrome, according to a new study that reveals the link between pain sensitivity and ocular surface health.
In a prospective clinical study, Rock O et al. investigated whether the pain triggered by commonly used diagnostic eye drops correlates with the presence and severity of dry eye syndrome. The findings, drawn from 33 patients undergoing routine evaluation at tertiary ophthalmology clinics, suggest that this frequently overlooked symptom may have diagnostic value.
Participants received either oxybuprocaine or tropicamide in each eye, and researchers recorded pain intensity using a visual analog scale along with the duration measured by stopwatch. These responses were then compared to standardized dry eye tests, including corneal fluorescein staining, tear break-up time, and Schirmer test results.
The study found that patients diagnosed with dry eye syndrome experienced significantly longer pain duration (P = 0.035), and those with severe dry eye reported higher pain intensity (P = 0.048). Notably, pain duration showed a significant correlation with corneal fluorescein staining (P = 0.027), a hallmark sign of dry eye.
In eyes exposed to oxybuprocaine, lower tear break-up time and Schirmer scores, indicators of tear film instability and reduced tear production, were significantly associated with increased pain responses (P = 0.021 and P = 0.037, respectively). For tropicamide-treated eyes, pain intensity was linked to functional limitations in daily activities (P = 0.042).
The authors suggest clinicians consider evaluating pain responses to diagnostic drops during routine eye exams. This low-cost, time-efficient observation could help flag patients who warrant further dry eye assessment and customized care plans.
Reference:
Rock O et al. Diagnostic Eye Drops and Pain Sensitivity: A Marker for Dry Eye Syndrome? Cornea. 2025. doi:10.1097/ICO.0000000000003893.