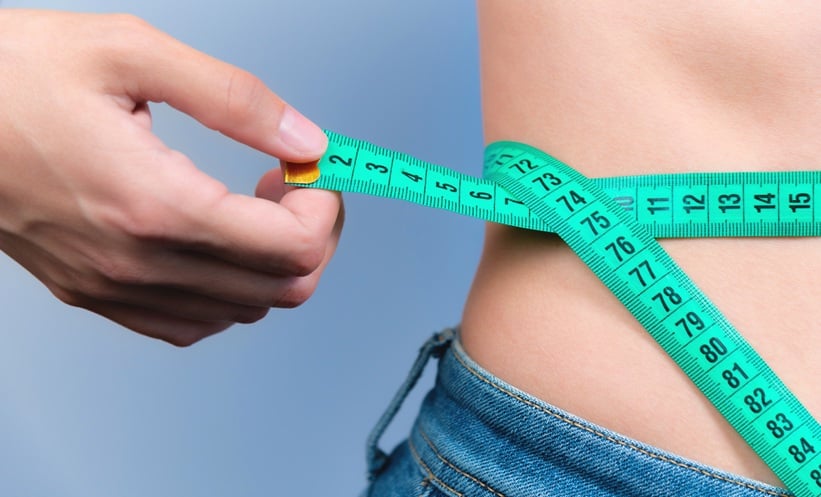
PSORIASIS, a chronic and inflammatory skin condition, affects millions globally and is increasingly linked to excess body fat, particularly fat stored around the abdomen. While the link between obesity and psoriasis is well-established, new research offers a more detailed understanding of how different types and distributions of body fat influence the risk of developing this disease.
Drawing on data from over 336,000 White British participants in the UK Biobank, including more than 9,300 individuals with psoriasis, researchers analysed 25 different measures of adiposity. These included traditional measures like body mass index (BMI) and waist circumference, as well as more advanced assessments such as bioelectric impedance and imaging techniques like dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry and magnetic resonance imaging.
The results revealed that central adiposity, fat concentrated around the waist and abdomen, had the strongest link to psoriasis. Among the top five measures most strongly associated with the disease, four focused on central fat. Waist-to-hip ratio and abdominal fat indicators showed particularly strong associations. Notably, overall body fat percentage also showed a significant effect, especially in women, suggesting sex-specific biological differences.
Importantly, the study explored whether genetics modified the relationship between fat distribution and psoriasis risk. Although individuals lacking the common psoriasis-associated gene variant HLA-C∗06:02 appeared more affected by central adiposity, further genetic analysis found no true interaction. This indicates that body fat and genetic risk contribute independently to psoriasis development.
These findings carry practical implications. Waist-to-hip ratio could become a valuable tool for identifying those at higher risk, especially as it may predict risk regardless of genetic predisposition. Moreover, the research supports incorporating fat distribution data into risk prediction models to better understand disease progression and severity.
Ultimately, the study reinforces the need for targeted weight management strategies and calls for further research into the biological mechanisms, such as inflammation and gut health, that may link central fat to psoriasis.
Reference
Ramessur R et al. Investigating the genetic basis of the influence of adiposity on psoriasis: a cross-sectional study in a large United Kingdom population-based biobank. J Invest Dermatol. 2025;DOI:10.1016/j.jid.2025.03.024